In this article you will learn what exactly is the difference between structure-borne sound systems and directly measuring ultrasonic sensor technology.
Injection molds are essential for the production of plastic parts. This is a process in which plastic granules are injected into a mold, which is then formed under high pressure and temperature. To ensure that the process works properly, sensors are required to measure important quality parameters during the filling process.
In the injection molding industry, there are two main types of sound sensors: Structure-borne sound sensors and direct-measurement ultrasonic sensors. Although both are used for monitoring the injection molding process, they differ in their operation and application.
In this article, the difference between structure-borne sound sensors and direct-measurement ultrasonic sensors in injection molds will be explained in more detail.
Structure-borne sound sensors
Structure-borne sound sensors are used to measure vibrations in the injection mold. They are usually attached to the mold frame or other structural elements of the mold and detect vibrations that occur during the injection molding process. These vibrations are an indicator of the functioning of the mold and can thus be used, for example, for the
- Condition-based maintenance of tools
- Tool damage detection
- or the tool qualification
be used.
This means that the structure-borne sound waves, which change as a function of the tool vibrations that occur, are interpreted and assigned to specific damage categories.
Structure-borne sound sensors can operate in several ways, including piezoelectric sensors, accelerometers, and laser Doppler vibrometers. Piezoelectric sensors convert vibrations into electrical signals, while accelerometers measure acceleration caused by tool vibrations. Laser Doppler vibrometers, on the other hand, measure the speed of tool vibrations by observing laser light, directing a laser beam at the surface and then analyzing the reflected radiation.
Direct measuring ultrasonic sensors (Moldsonics Sensorik)
Direct-measurement ultrasonic sensors are used to measure quality parameters directly on the injection molded part, i.e. directly on the resulting product.
They are usually placed at critical and quality-relevant positions in the injection mold and record a characteristic ultrasonic response curve of the injection and holding pressure process.
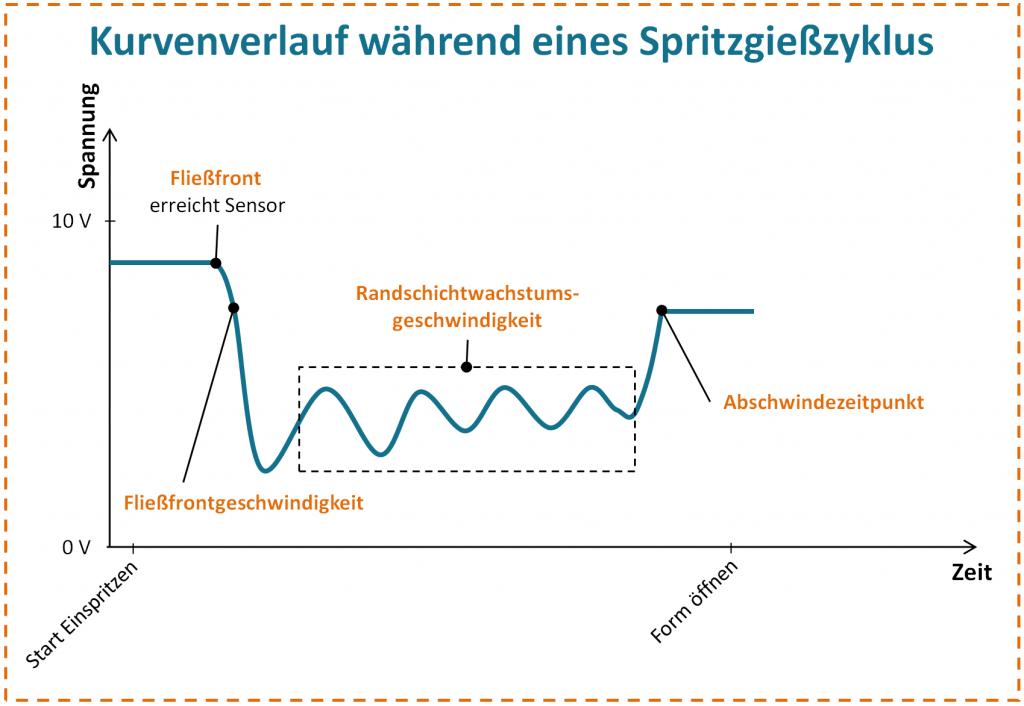
Characteristic ultrasonic response curve when using directly measuring ultrasonic sensor technology
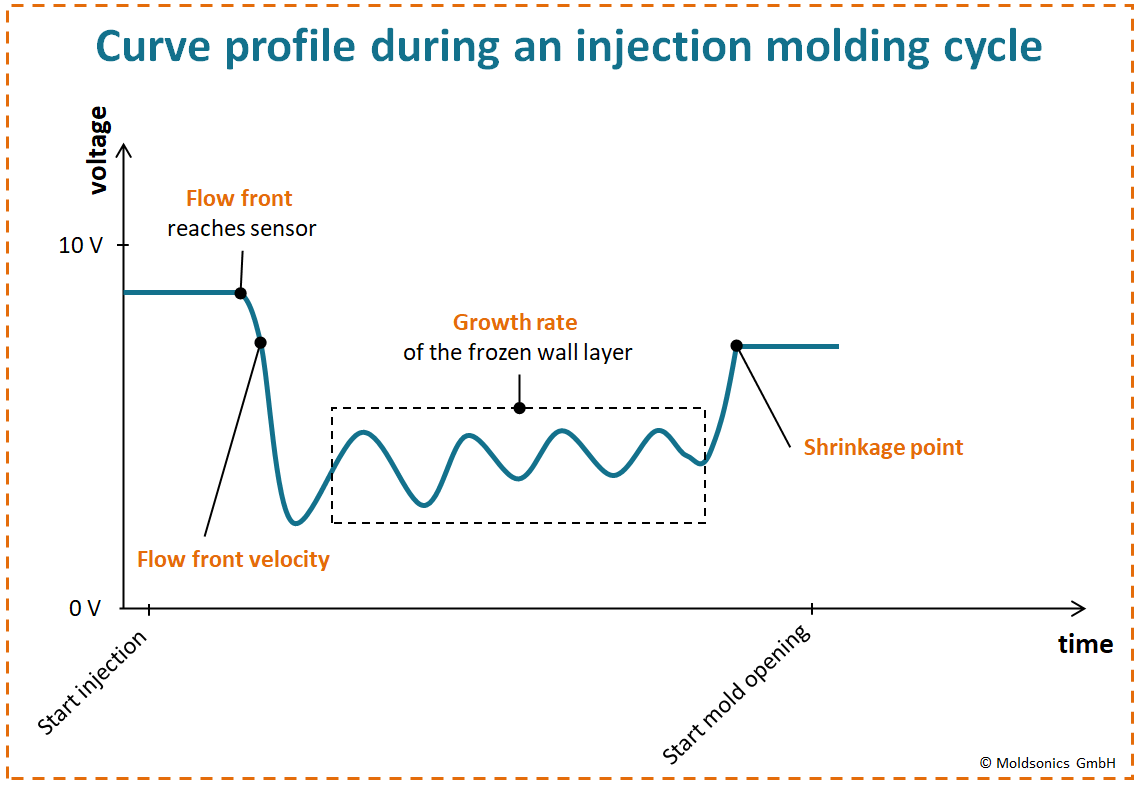
Characteristic ultrasonic response curve when using directly measuring ultrasonic sensor technology
The mode of operation is based on the permanent emission of ultrasonic waves and the analysis of the reflected waves. These sensors use the piezoelectric effect to generate electrical signals when they are loaded by electrical voltage and, conversely, to generate sound waves when they receive electrical current.
The ultrasonic waves emitted by the sensors are reflected by the cavity wall and the plastic melt to be measured and return to the sensor. Based on the time it takes for the ultrasonic waves to return and the intensity of the reflected ultrasonic pulse, the sensor can determine a wide variety of quality-related parameters. These include:
- The flow front detection, i.e. when the melt front reaches the sensor position
- The velocity of the melt flowing by
- The solidification rate of the cooling plastic material
- The shrinkage of the plastic component from the cavity wall
- The thermal equilibrium of the injection mold
The use of this direct measuring ultrasonic sensor technology in the injection molding industry is completely new. To date, the measurement of a characteristic ultrasonic response curve can only be achieved with Moldsonics' sensor technology and is therefore unique.
The use of this sensor technology is not limited to individual industries and is currently already being used in a wide variety of industries, including the medical industry, the automotive industry, the food industry and the toy industry, to name just a few.


